Classification Of Computer Networks
By way of organization, the network is divided into real and artificial.
Artificial networks (pseudonets) enable computers to be linked together through a whale pair, and previously used successive or parallel ports, and do not need additional devices. Artificial networks are used when information needs to be downloaded from one computer to another.
Real networks It is possible to link computers by means of special switching devices and the physical environment of data transmission.
The variety of computer networks can be classified according to the cluster of topics:
(1) Territorial prevalence;
(2) Ownership;
(3) Information speed;
(4) Type of transmission environment;
(5) Topology;
(6) Computer interface.
The network can be local, global and regional in terms of its territorial prevalence.
Local is networks within one building.
Regional - located in the city or areas.
Global in the territory of a State or group of States, such as the world Internet.
The term " corporate network " is also used in the literature to describe the interconnection of several networks, each of which can be built on various technical, programme and information principles.
Local networks are closed-circuit networks and only a limited number of users are allowed access to them for whom the network is directly linked to their professional activities. Global networks are open and serviced by all users.
Ownership
The supplies differ between departments and public networks♪ The offices belong to and are located within the organization. Public networks are networks used in State structures.
Transmission speed
At the rate of transmission, computer networks are divided into low-, medium- and high-speed.
- low speed (up to 10 Mbit/s),
- Average speed (up to 100 Mbit/s),
- High-speed (over 100 Mbit/s);
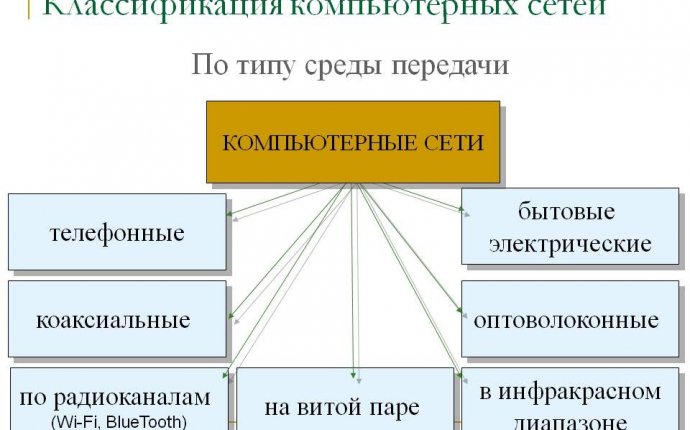
Type of transmission environment
By type of transmission environment, the network shall be divided into:
- Locational, whale, fibre optic;
- wireless, with radio channels, infrared.
The network unit is a computer or a network switching device. The branch of the network is a route connecting two related nodes.